Over 600,000 people in the UK have epilepsy.
Epilepsy is a common and serious neurological condition which affects the brain and nervous system. Seizures always start in the brain and are caused by many different underlying causes, including a person's genetics, a structural change in the brain or from other underlying conditions.
There are over 40 different types of seizure, and not all of them are physical which is why epilepsy can also be an invisible condition.
On this page you'll find information around all aspects of epilepsy including causes, triggers, diagnosing epilepsy and treatment.
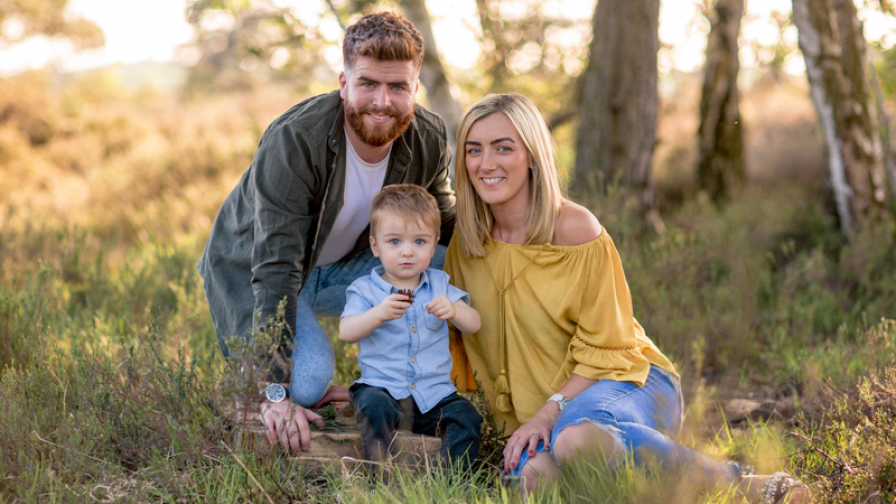
Shown on the right is Mel Allen with her family. Mel was diagnosed with epilepsy and found treatment and support from Epilepsy Society.
What is epilepsy?
Living with epilepsy
Having seizures, or being told “you have epilepsy”, can affect people in different ways. This includes driving, sleep, work and travel.
Epileptic seizures
There are many different types of epileptic seizure. Any of us could potentially have a single epileptic seizure at some point in our lives. This is not the same as having epilepsy, which is a tendency to have seizures that start in the brain.
What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy varies greatly and affects everyone differently. If you or someone you know has epilepsy, you may find it helpful to learn more. Here are some basic facts about epilepsy and where to get more information.
Diagnosing epilepsy
How epilepsy is diagnosed
Diagnosing epilepsy is not simple. Doctors gather lots of different information to assess the causes of seizures. If you have had two or more seizures that started in the brain you may be diagnosed with epilepsy.
Just diagnosed
There can be a lot of misunderstanding about epilepsy and seizures, but it is a common condition. About one in a hundred people has epilepsy, so you may already know people with the condition. This page aims to help you learn more about epilepsy, to understand how it might affect you, and answer some questions you might have about living with the condition.
How do you treat epilepsy?
Anti-seizure medication (ASM)
This information is for both adults and children with epilepsy and answers some questions you might have about anti-seizure medication. Where we talk about controlling seizures or ‘seizure control’ we mean stopping seizures from happening.
Epilepsy surgery
Brain surgery or neurosurgery is one way of treating epilepsy. Certain criteria have to be met and tests have to be done to assess suitability.
Epilepsy treatment
If you have just been diagnosed with epilepsy, you may have questions about medication and treatment.
Looking after your wellbeing
Diet and nutrition
A balanced diet from different food groups helps the body and brain to function, helping us to stay healthy. This may help reduce the risk of seizures for some people with epilepsy.
Links between epilepsy and mood
For some people, their epilepsy and mood problems are not connected, they just happen to have both conditions. However, potential links are to do with how epilepsy affects your life as well as with your brain, your genes and your family history.
Do you know what to do if someone has a seizure?
Are you #seizuresavvy?
Our #seizuresavvy campaign focuses on tonic clonic seizures as these are the type of seizure that are most easily recognised. The charity’s new campaign gives people three simple but key instructions to remember in an emergency: “Calm, Cushion, Call.”
The recovery position
Our step-by-step guide to the recovery position shows you how to help someone recover after a tonic clonic seizure. These steps should be followed once the shaking has stopped.
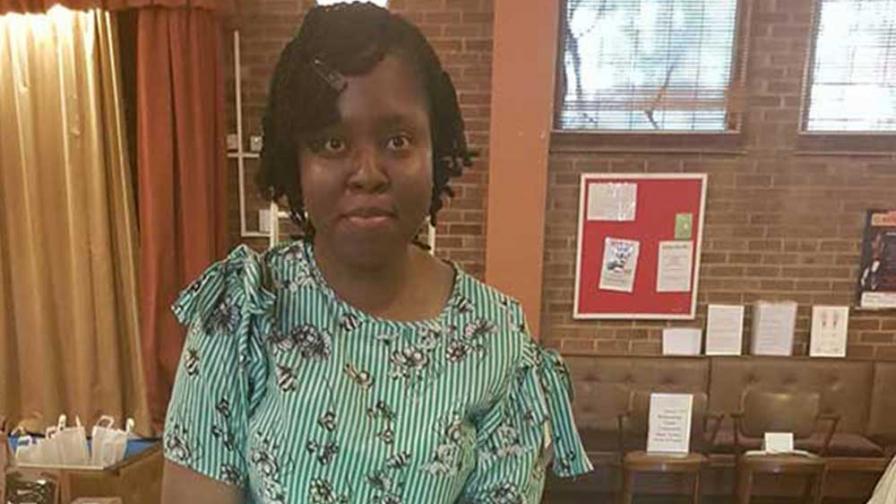

Personal stories
Find out more from people who have been affected by epilepsy in our inspiring personal stories section.
Want to know more?
Download our What is epilepsy? leaflet